Selecting the right rock bolt is essential for safe and efficient underground construction, mining, or tunneling projects. Rock bolts are critical for stabilizing rock formations, preventing collapse, and protecting workers and equipment. A well-chosen rock bolt specification balances strength, durability, and installation efficiency, while a poor choice can lead to structural failures, costly repairs, and delays. Careful planning ensures the ground support system performs reliably throughout the project life cycle.
What is a Rock Bolt?
A rock bolt is a long steel rod or bar designed to anchor unstable rock layers to more stable strata, transferring loads and preventing rock movement. It plays a vital role in tunnels, mines, and other underground works where natural rock integrity cannot be guaranteed. The correct type, size, and strength are selected through engineering analysis to make sure the bolt can handle both short-term installation loads and long-term ground pressure. By providing reinforcement deep inside the rock mass rather than just on the surface, bolts create a safe environment for workers and protect expensive machinery from rockfalls.
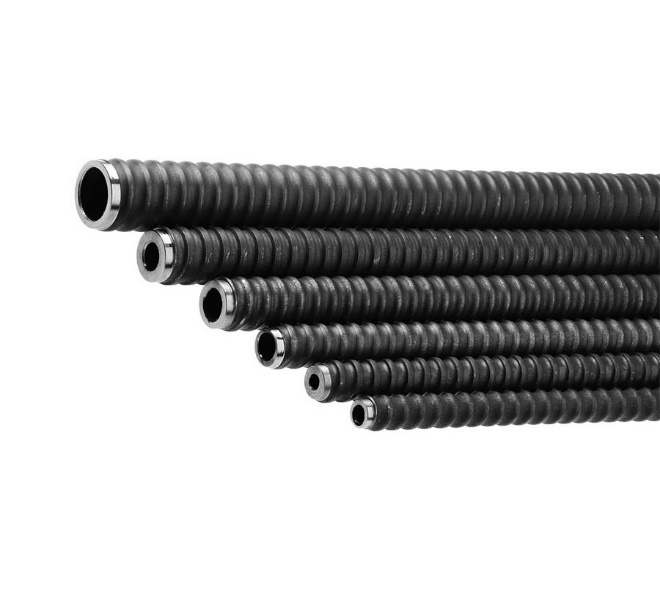

Key Factors to Consider
- Material
Standard carbon steel bolts offer a balance of strength and cost-effectiveness, galvanized steel provides enhanced protection against moisture and rust, while composite bolts deliver reliable performance in harsh or chemically aggressive ground conditions. - Length and Diameter
Both dimensions are specified according to ground conditions. Longer bolts extend into more stable rock layers to provide reliable anchorage, while larger diameters increase load-bearing capacity. Proper sizing is essential for ensuring that bolts meet structural requirements without adding unnecessary cost or installation difficulty. - Strength and Load Capacity
In defining a rock bolt specification, engineers carefully assess expected ground pressures, installation techniques, and safety margins to ensure each bolt can reliably handle peak loads with sufficient reserve for long-term stability. - Anchoring Method
Mechanical anchors, resin-anchored bolts, and friction bolts each have distinct benefits. Mechanical anchors allow quick installation, resin anchors create strong bonds in fractured rock, and friction bolts adapt to variable ground conditions. Choosing the appropriate anchoring method guarantees that each bolt functions reliably under real-world conditions and achieves its intended performance. - Corrosion Protection
Underground moisture accelerates rusting, reducing service life. Using bolts with protective coatings, hot-dip galvanization, or inherently corrosion-resistant materials helps maintain long-term performance and minimizes maintenance needs, which is especially important in permanent installations.
Why Proper Selection Matters
- Improved safety and reliability– Correctly specified rock bolts prevent rockfalls, surface spalling, and deeper ground deformations that can compromise structural stability. A properly engineered system keeps workers safe, protects expensive equipment, and reduces the likelihood of accidents in high-risk underground environments.
- Lower long-term costs– Choosing the right specification from the start reduces premature failures and the need for unplanned replacements. This minimizes maintenance budgets, avoids costly project interruptions, and helps extend the overall service life of the support system.
- Optimized material and installation efficiency– When each bolt is sized to carry its intended load, resources are used efficiently without unnecessary oversizing. This not only saves material costs but also makes drilling, grouting, and installation faster and less labor-intensive.
- Higher project performance and scheduling control– A well-designed ground support system reduces unexpected delays by ensuring predictable behavior of the rock mass. Stable ground conditions help excavation, lining, and subsequent construction phases stay on schedule and within planned timelines.
- Compliance with safety and engineering standards– Meeting proper design requirements helps contractors satisfy local regulations and industry guidelines, reducing the risk of fines, rework orders, or liability issues while maintaining a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Safe installation of rock bolts requires careful evaluation of multiple factors including material selection, bolt dimensions, tensile strength, anchoring system, and environmental conditions such as groundwater or corrosive elements. When these aspects are properly analyzed and combined into a clear rock bolt specification, the result is a support system that maintains long-term stability, safeguards workers and equipment, and delivers consistent performance even under extreme geological stresses. By investing time in accurate specification at the design stage, projects achieve better safety outcomes, longer service life of components, and greater overall cost efficiency.
For more information on choosing the right rock bolt specification for your project, feel free to visit ONTON for expert guidance and support. For inquiries or to discuss the specific requirements of your project, feel free to reach out to us anytime for expert assistance.





