Hot-dip galvanized anchor bolts play a vital role in securing structural members such as columns, beams, and machinery to concrete foundations.
Proper installation of these bolts is essential to ensure structural stability, long-term performance, and safety. Following professional guidelines can help avoid common problems such as misalignment, insufficient embedment, and premature corrosion.
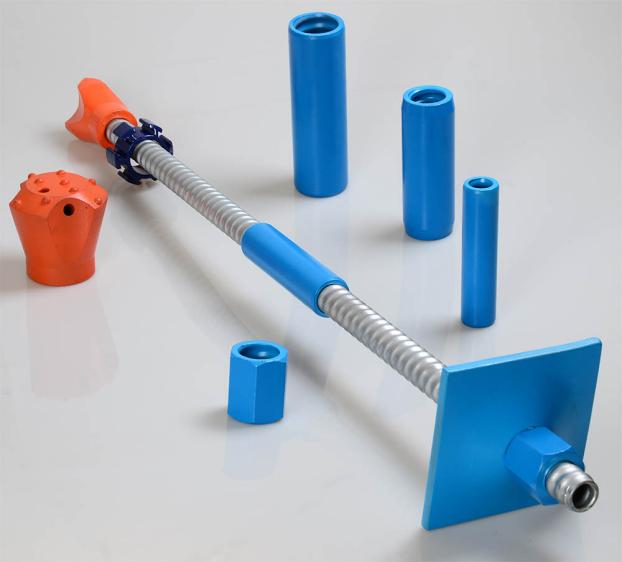

Preparing for Installation
- Before starting the installation, it is important to prepare the worksite and the materials. Hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts should be inspected for damage or coating defects.
- Any scratches, dents, or irregularities on the galvanization layer can compromise corrosion resistance.
- Ensure that the bolts meet the required specifications for size, thread type, and length based on the project requirements.
- The foundation area should be clean and free from debris, dust, or moisture. Proper formwork and concrete molds should be prepared to hold the bolts in position during the concrete pour.
- Using templates or jigs can help maintain accurate spacing and alignment for multiple bolts, especially when securing large structural components.
Positioning and Alignment
Misalignment can lead to structural issues and make it difficult to connect beams, plates, or machinery. Using measurement tools such as levels, laser guides, or plumb lines ensures the bolts are positioned correctly. The bolts should extend vertically or according to the specified angle in the design plans.
When using templates, make sure they are securely anchored to prevent movement during the concrete pour.
Embedment and Concrete Considerations
- The performance of hot dipped galvanized anchor boltsis influenced by their embedment depth and the quality of the surrounding concrete.
- Embedment depth should comply with engineering specifications to provide sufficient anchorage. The bolts must be fully embedded in concrete without contact with voids or air pockets, which can weaken the connection.
- Vibrating concrete is standard practice to remove air pockets, but it should be done carefully around the bolts to prevent movement.
- Concrete curing time is essential; the bolts should not be subjected to loads until the concrete has reached the required strength, typically specified by the structural engineer.
Protecting the Galvanization
- During installation, it is important to protect the hot dipped galvanized coating from damage. Scratches or chipping can reduce corrosion resistance.
- If minor damage occurs, it can be treated using zinc-rich paint or galvanizing repair compounds recommended for field use. Avoid abrasive handling and do not use wire brushes or harsh chemicals that can degrade the galvanization layer.
- Environmental conditions also affect the longevity of hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts. For outdoor or high-humidity environments, ensure that bolts are not exposed to water accumulation during installation. Temporary covers or protective coatings can prevent corrosion before the structure is completed.
Tightening and Final Adjustments
Once the concrete has cured and the structure is ready, the hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts can be tightened.
Nuts and washers should be applied according to engineering specifications. It is important to avoid overtightening, which can distort threads or damage the bolt, and undertightening, which can compromise the connection. Torque wrenches are recommended for accurate tightening.
For critical applications, periodic inspections are advised after installation to ensure bolts remain secure and free from corrosion. This is especially important for industrial machinery, bridges, or other structures subjected to vibration, heavy loads, or environmental stress.
Common Installation Challenges
- Several challenges can occur during the installation of hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts. Using templates, careful measurement, and protective handling techniques minimizes these risks.
- Additionally, coordination between construction teams is important to ensure proper timing for concrete pouring, curing, and bolt installation.
- Environmental factors such as rain, high humidity, or extreme temperatures can also affect installation. Planning for these conditions, including temporary protective measures, ensures that the hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts maintain their corrosion resistance and structural performance.
Advantages of Proper Installation
Correct installation of hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts ensures maximum performance and durability.
- Properly positioned and embedded bolts provide strong anchorage for structural elements, reducing the risk of failure.
- Protecting the galvanization during installation prevents premature corrosion, even in harsh environmental conditions.
- By following professional installation guidelines, construction teams can achieve safer, more reliable, and long-lasting structures.
Moreover, welled anchor bolts reduce maintenance needs and extend the life of the structure. This is particularly important in infrastructure projects such as bridges, towers, and industrial facilities, where safety and durability are critical.
Conclusion
Preparing the worksite, ensuring accurate positioning, maintaining correct embedment, protecting the galvanization layer, and following proper tightening procedures are all critical steps.
By adhering to installation guidelines, construction professionals can maximize the lifespan and reliability of hot dipped galvanized anchor bolts.
Careful handling, attention to environmental conditions, and adherence to engineering specifications ensure that these bolts provide long-term stability, safety, and durability for a wide range of structural applications.





