The growth of using self-drilling anchor hollow bar in rock bolting, soil nailing and micropiling is rapid.
Self-drilling anchor has been around for at least 40 years.
It is developed for tunneling applications in weak or collapsing ground.
Until today it is still used for the NEW Austrian Tunneling Method (NATM).
However,
Unlike the solid reinforcing bar, criteria for self-drilling hollow bars were not perfect in the past.
Manufacturers had only concerned about loading capacity and surface profile.
You must know solid rebar is required to achieve specific strength, while maintaining excellent ductility.
Ductility means deformations without breaking, plastic, visible deformation until rupture.
It is an important index in construction, represents the safety factor of structure.

Similarly,
Reinforcing is the core function of self-drilling anchor hollow bars, enough elongation ductility should be required.
That’s why now you can find elongation Agt is introduced in the latest version of DSI DYWI Hollow Bar Drill Rod Manual, Orica MAI SDA self-drilling anchors catalogue, and ISCHEBECK Titan Hollow Bar Requirement, etc.
Now you can get a checklist for the reference of choosing a standard self-drilling anchor hollow bar:
- Yield load of finished hollow bar
- Ultimate load of finished hollow bar
-
Elongation Agt (ductility) up to ultimate without reduction in cross-section of finished hollow bar
So what should you ask suppliers to provide?
Tips:
- Test reports from independent laboratories. For instance, SGS.
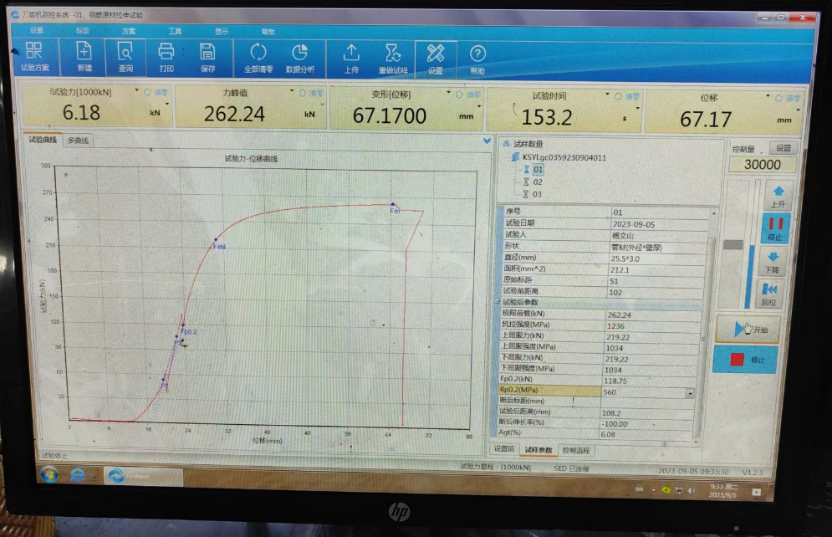
- Test results include Stress/Strain Diagram, tensile strength and elongation Agt.
- Bended sample of self-drilling anchor hollow bar.
All the information is outlined in detail in the report which is given by ontonbolt. A leading manufacturer of self-drilling hollow bars, used for strengthening the grounds.
So, what is required in the standard of American ASTM?
In the Standard Specification for Deformed and Plain Billet-Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement, it recommends bending test for hollow bar anchors.
The test is a good way to measure the ductility of a grout bonded anchors on site. (The ductility also can be checked by a tensile test which calculates Agt)
For the concrete reinforcement work of civil ground engineering, ASTM A615 has proposed the details of a bending test for steel bars.
To be brief, the standard demands the reinforcing material shall withstand being bent around a pin without cracking on the outside radius of the bent portion.
The requirements for degree of bending and sizes of pins are below:
Bend Test Requirement of Hollow Bar Anchors
For hollow bar anchors, bending around 180 degrees (U shape) over a pin diameter D > 6 x Diameter is required. Furthermore, there shouldn’t be any visible cracks or hollow bar breaks.
The ductility of hollow bars can be checked easily on site by a bend / rebend test:
Bending around 180° (U-shape) over a pin diameter D ≥ 6 x diameter of hollow bar e.g. for ONTON R32N D = 6 x 32 mm = 192 mm.
If there are visible cracks or the hollow bar breaks, there is not enough ductility as required in detail in ASTM A 615. “Specification for Low-Alloy Steel Deformed and Plain Bars for Concrete Reinforcement”.
Bending Test hollow bar
For the recent years, the grouting concrete anchor bars are applied in micropiles, soil nails, wall tie down and tieback anchor systems, etc. And there have been existing standards in Europe and America for these applications.
Self-drilling hollow bars with high ductility are the reliable protections for civilians in case of earthquake and other disasters happen.
All ONTON hollow bar anchors can pass this bend test easily, benefiting by its high ductility. And in the same time, there isn’t any loss of its strength performance.


