Abstract
The foundation of construction support continues to improve to meet the requirements of building and structures, since people began to build constructions.
With the expansion of cities, there are not enough support areas near the grounds. Therefore, foundation is designed to transfer load to a suitable bearing earth layer.
Buildings influenced by wind and earthquake are higher and narrower. Their foundation should bear compressive load and forces from vertical and horizontal direction.
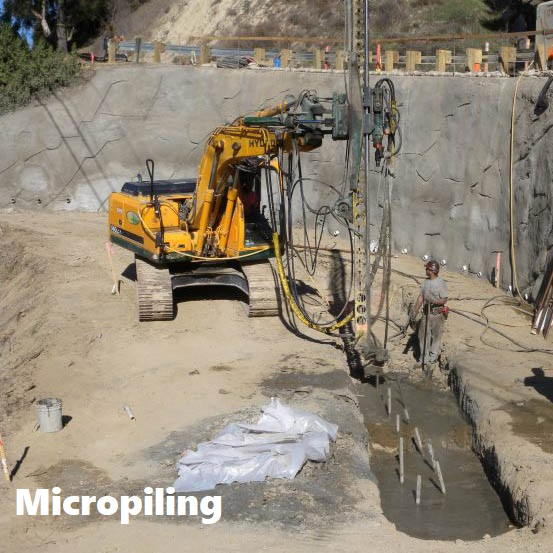
Large concrete foundation requires larger area and excavation, while small and deep drilling or piling becomes a more competitive option. The main composition is concrete and cement with embed rebars.
Micropile belongs to this kind of foundation. The structure of micropile is very simple, and the design and installation is unique. Micropile has been used more and more widely.
Evolution of micropile
Micropile was invented by Dr. Fernando Lizzi in 1950s. Since then a variety of micropile systems had been developed, using a combination of rebars/cement, some assembled with steel case.
Lizzi designed pile group to form the foundation. These piles reinforce the earth as the root. That’s why Dr. Lizzi named it root-pile.
You can find a graphic of root-pile at onton’s previous article The top 5 things you should know about hollow bar micropiles
Since then a lot of installation and reinforcement methods are developed. It is necessary to generalize the variety of pile foundations. They are called minipile in the first, then changed to micropile.
The International Workshop on Micropiles (IWM) was established in 1994. And micropile became more and more famous in the area of geotechnical and foundation engineering in north American. Later it spreads to the worldwide. Micropile is mainly applied as friction pile, to bear tension and/or compress load.
What is micropile?
Micropiles are normally in the diameters of 60 to 300mm. They are often used for underpinning, drilling and grouting. In the middle of Micropiles are usually reinforcing bars, one piece or several.
The reinforcing bars are solid or hollow core. All thread, can be cut into any length.
What is the unique of micropile?
Micropiles can be installed with little drilling equipment. They are especially useful at sites with difficult or restricted access, or environmental sensitivity.
For example, TITAN IBO can be installed with only a rotary drilled rig. This way can reduce or eliminate the vibrations which may cause structural damage. While other methods use heavy impacting and piling will bring vibrations. It is likely to cause structural damage, particularly in or near the buildings.
GEWI Pile
Dr. Thomas Herbst, who was the leader in geotechnical engineering, developed the concept of Gewi pile.
GEWI is originated from the German word GEWINDE or THREAD.
Gewi thread bars are installed by inserting into a borehole or a sleeve pipe. Afterwards, the borehole is filled or pressure grouted with cement mortar from the bottom up. The grout simultaneously serves for transferring forces to the soil by skin friction and as standard corrosion protection (SCP). Grouting can be repeated several times, until the pressure or skin friction is fulfilled.
Pin Pile
Nicholson Construction Company developed Pin Piles in 1970s.
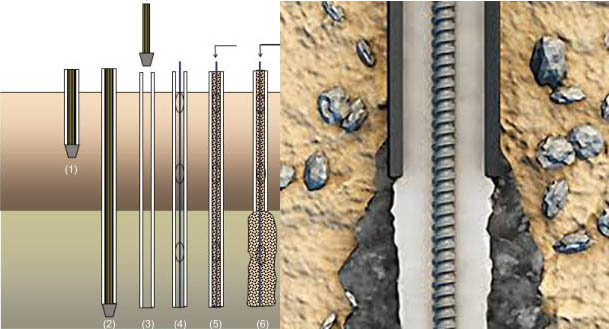
Stages in the construction of a standard pin pile (Figure):

Stages in the construction of a standard pin pile
Pin Pile System places drill casing to fix the boring hole. The inner drill rod is used fro flushing or deeper drilling. After grouting, the case is pulled out from the borehole.
Pin Pile also can be applied to post-grouting systems.
TITAN/IBO self-drilling injection micropile
Steps of micropile installation:
- Drill hole
- Place reinforcing bars
- Grout
One of the latest construction methods is integrated 3-in-1 installation. This method uses hollow bar anchor, ie., self-drilling anchor SDA. Sometiems solid rebars or steel strand are placed in the hollow core.
Injection Boring Pile (IBO) is co-developed by Friedrich Ischebeck Gmbh Company and Con-Tech System Company. It evolved from rootpile, provide functions for drilling, grouting and reinforcing.
Titan IBO pile and soil is fully integrated into a whole. Especially installed in groups, they constitute a foundation system of reinforcing soil.
The TITAN IBO injection pile is combined with a hollow bar as the drilling rod, and a special sacrificial drill bit. The rotary percussive drilling, grouting and injection are operated in a single step. All drill bits have jet openings which allows pressure grouting while the drilling.
In the process of drilling and grouting with hollow bark, the hole is cleaned out by continually flushing. By this way, the bore hole place is stable, no loose or collapse of the ground, and the high quality of grouting cement.
Below is the components of a typical TITAN IBO micropile.
Titan IBO Micropile
The basic purpose of TITAN IBO is to install high performance pile with small drilling rigs. It can be operated in a limited room of overhead space. And it can be used for the reinforcement of existing foundations.
Corrosive Protection
Apart from cement grouting, there are several ways to provide extra corrosive protection.
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG)
Reinforced anchor bars can be protected against corrosion by hot dip galvanizing in accordance with ASTM A-153.
The coated Zinc is common and relatively cheaper. While the steel is in the kettle, the iron in the steel reacts with the molten zinc to form a tightly-bonded alloy coating that provides superior corrosion protection to steel.
Hot-dip galvanizing protects steel catholically similarly to the sacrificial anode method.
The thickness of zinc coating should be strictly controlled to ensure the specification of threads. In most cases, the female thread dimensions of nuts or couplers should be larger than usual. And this may reduce the load carrying capacity.
Epoxy coating
Soil nails or micropiles can be protected against corrosion by epoxy coating in accordance with ASTM A-934, ASTM A-775 or AASHTO No. M284. The thread profile requires enlargement. And the damage of coating has to be avoided.
Double Corrosion Protection (DCP, not applicable to hollow bar)
This method is mainly applied in workshops, to thread steel bars or all-threaded bars. This type of corrosion protection is a part of Dywidag GEWI pile and ground anchor THREADBAR technology.



